.png)


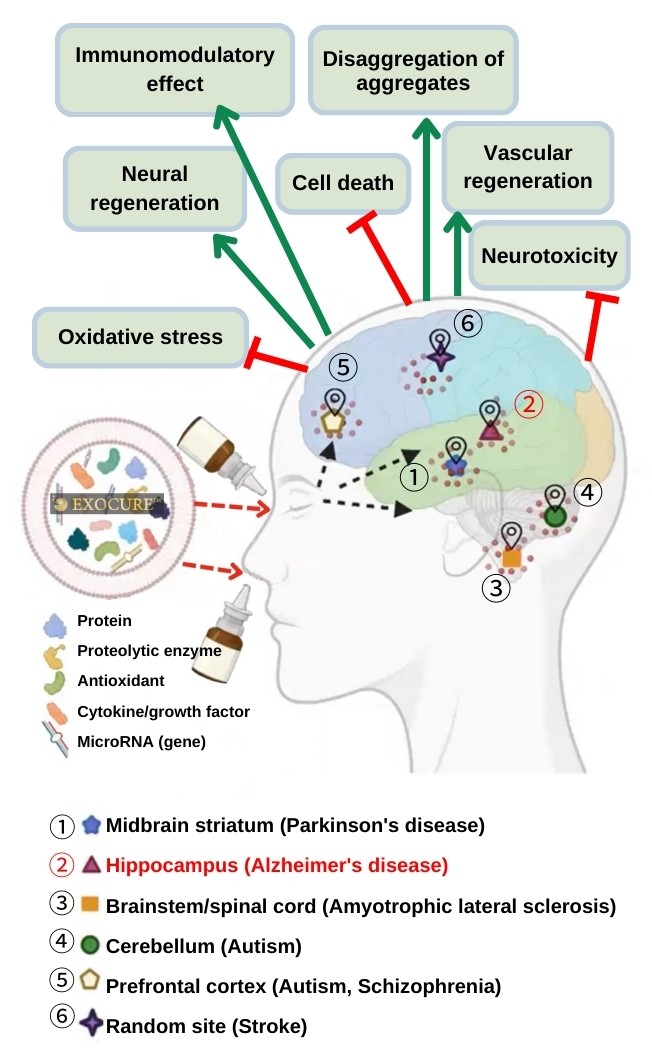
The olfactory pathway from the nasal olfactory epithelium to the olfactory bulb, recognized for its high utility in delivering drugs to the brain, is targeted for the administration of EXOS formulations. This is expected to lead to enhanced cognitive function through effects such as neuroprotection, axonal elongation, modulation of neurotransmission, suppression of inflammation, and regulation of microglia.

EXOCURE can reach the brain after intranasal administration and ocular absorption. Blood-brain barrier
What substances can cross the blood-brain barrier?
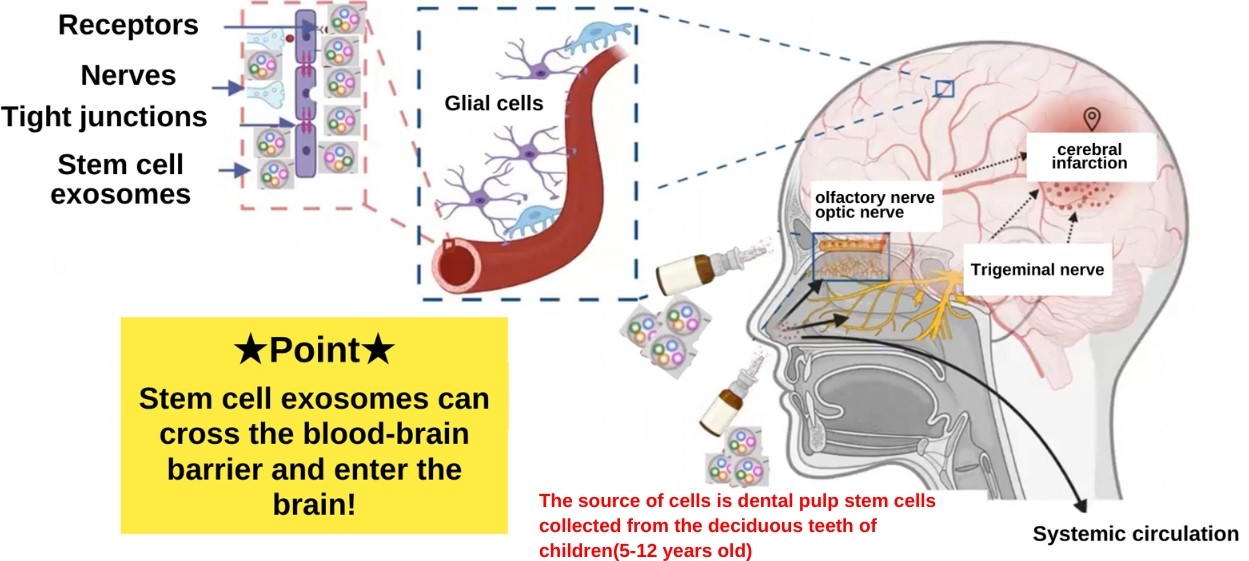
Exosomes from nasal and eye drops enter the brain through the olfactory and optic nerves, which extend directly from the brainstem.
Other than exosomes, only small molecules such as glucose and amino acids, which are the source of brain activity, can cross the blood-brain barrier and enter the brain through blood vessels.
Larger molecules such as drugs cannot cross the blood-brain barrier. Thus, even if certain drugs are known to be beneficial to the brain, it remains difficult to get them to the brain. This is why there is so much research on drugs in the brain.
The olfactory and optic nerves are among the 12 pairs of nerves (peripheral nerves) in the brain.
Nasal inhalation and ocular absorption of stem cell exosomes hold promising potential.