
Top stem cell therapy clinics in Japan are now switching to Exocure.
Authorized Dealer in Hong Kong
.jpg)
1
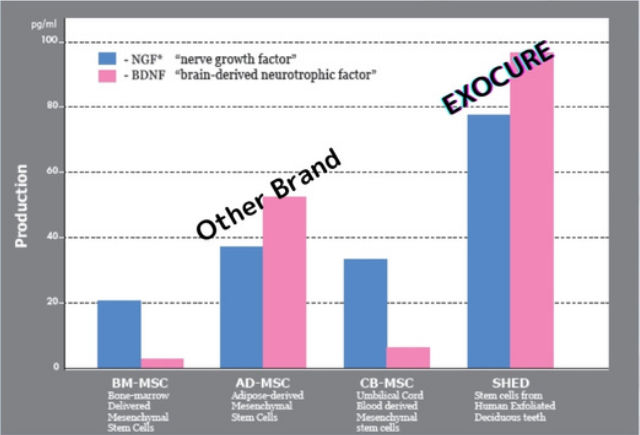
The source of cells is
dental pulp stem cells collected from
the deciduous teeth
of children(5-12 years old), which are suitable for preemptive self-repairing
medicine in every aspects, with a traceable collection route and without
disease history problems.
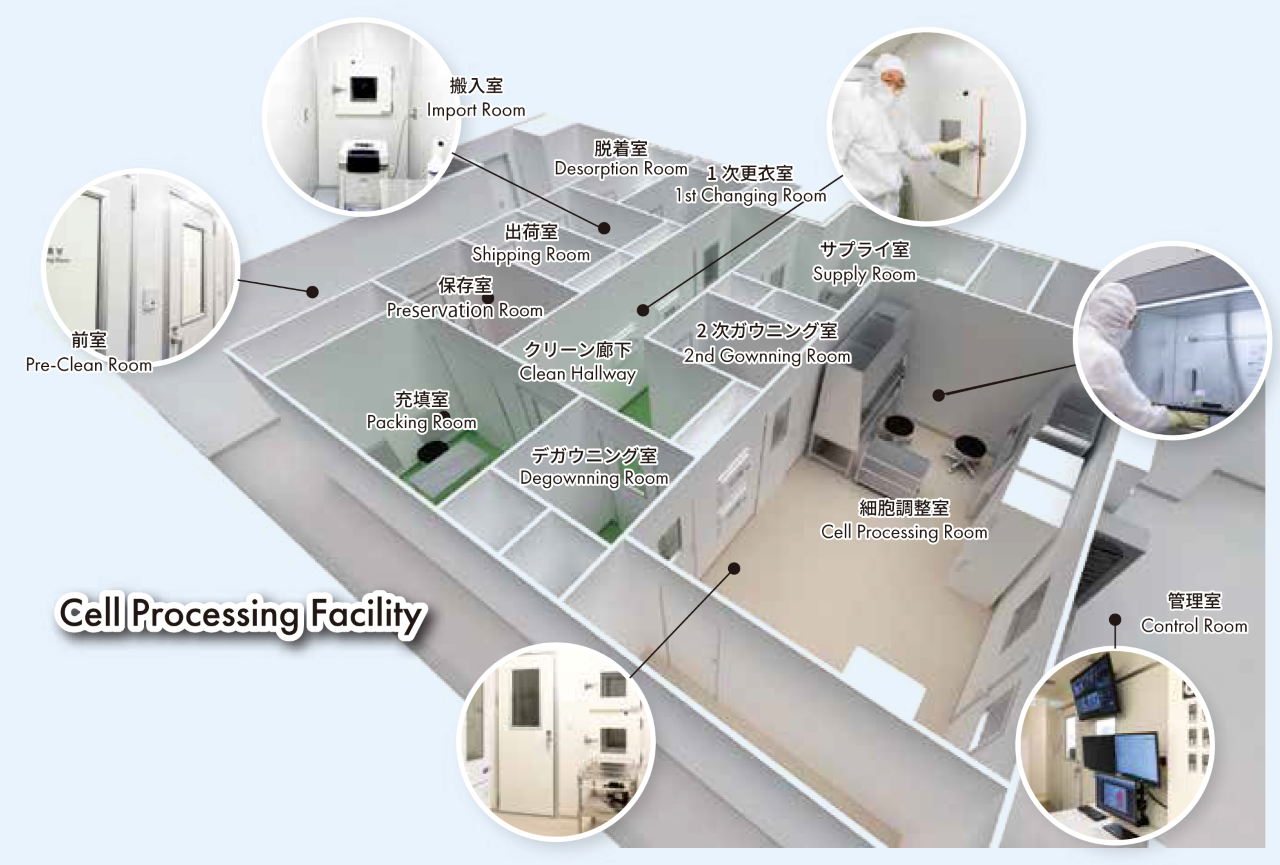
「E-GIC HANEDA」 IN JAPAN
The E-GIC HANEDA facility is focused on advancing exosome research. Within the facility, there is a laboratory that has established a GMP-compliant Cell Processing Facility (CPF). The CPF is designed to investigate the efficacy and safety of new medical technologies and treatments that are developed through the research conducted at the facility. Furthermore, the facility also houses a member-based clinic that can carry out clinical research to work towards the practical application of the research outcomes.
The E-GIC HANEDA facility is focused on advancing exosome research. Within the facility, there is a laboratory that has established a GMP-compliant Cell Processing Facility (CPF). The CPF is designed to investigate the efficacy and safety of new medical technologies and treatments that are developed through the research conducted at the facility. Furthermore, the facility also houses a member-based clinic that can carry out clinical research to work towards the practical application of the research outcomes.
2


3
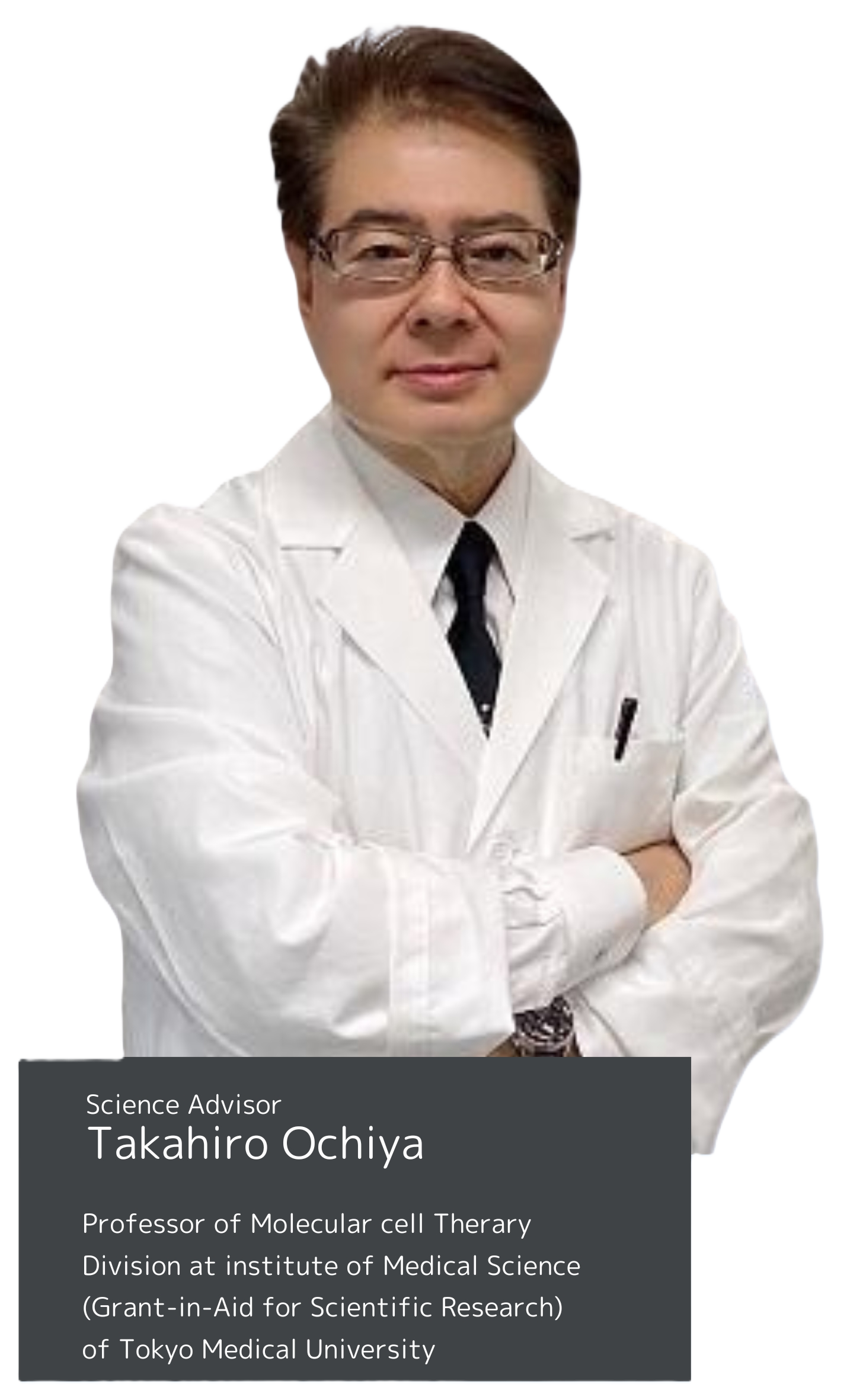
Professor Takahiro Ochiya of the Medical Research Institute at Tokyo Medical University has been ranked #1 in the world for extracellular vesicle (exosome) research by two independent organizations, ExpertScape and Scholar GPS.
Professor Ochiya, from the Division of Molecular and Cellular Therapy at the Future Medicine Research Center of the Medical Research Institute at Tokyo Medical University (President: Yukiko Hayashi), has been ranked #1 globally in the researcher rankings for extracellular vesicle (exosome) research by both the ExpertScape and Scholar GPS organizations. Additionally, Lecturer Yusuke Yoshioka from the same division has been ranked 5th and 13th respectively.
While there are various methods used to objectively quantify researchers' achievements, Professor Ochiya has been selected as one of the top 0.1% of researchers worldwide in Clarivate Analytics' Highly Cited Researchers (HCR) list for 5 consecutive years since 2019. These evaluations reflect the globally recognized excellence of Tokyo Medical University's research achievements in the field of extracellular vesicles. Going forward, our university will continue to pursue exosome research as part of our efforts to develop patient-friendly (minimally invasive) medical treatments.
Professor Ochiya, from the Division of Molecular and Cellular Therapy at the Future Medicine Research Center of the Medical Research Institute at Tokyo Medical University (President: Yukiko Hayashi), has been ranked #1 globally in the researcher rankings for extracellular vesicle (exosome) research by both the ExpertScape and Scholar GPS organizations. Additionally, Lecturer Yusuke Yoshioka from the same division has been ranked 5th and 13th respectively.
While there are various methods used to objectively quantify researchers' achievements, Professor Ochiya has been selected as one of the top 0.1% of researchers worldwide in Clarivate Analytics' Highly Cited Researchers (HCR) list for 5 consecutive years since 2019. These evaluations reflect the globally recognized excellence of Tokyo Medical University's research achievements in the field of extracellular vesicles. Going forward, our university will continue to pursue exosome research as part of our efforts to develop patient-friendly (minimally invasive) medical treatments.