The good thing about anti-aging is that you can stay young and look much younger than your age. People want to stay young forever, and by keeping young with anti-aging, you can keep your mind and body healthy.
Exosome
Exosomes are extracellular vesicles (particles of about 100 nanometers) that have a lipid double-membrane structure that plays an important role in maintaining life, secreted by abnormal cells, including fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and blood cells, as well as cancer cells.
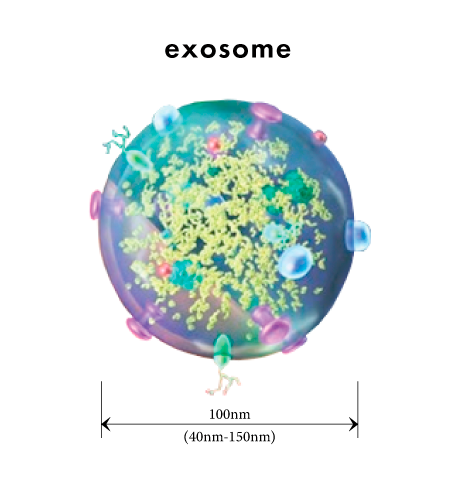
When it was first discovered in 1983, exosomes were thought of as "garbage bags" that release waste products out of the cells.
However, with the remarkable progress made in the last decade triggered by a study report of the inclusion of miRNA (microRNA) in the exosomes in 2007, it is said that it will "fundamentally change the treatment of all diseases". It also has become the subject of much attention by researchers around the world.
In fact, when the role of exosomes is elucidated one after another, it may affect the onset / exacerbation mechanism of various diseases including cancer, Alzheimer's disease, neurodegenerative diseases, and lifestyle-related diseases such as diabetes. The value of exosomes is now beginning to expand into diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Communication between cells and organs
Until now in medical common sense, it has been thought that the brain is the control of the human body, and all other organs are in accordance with it.
However, exosome research has made it necessary to reconsider the fundamentals of the human body.
Good Exosomes and Bad Exosomes
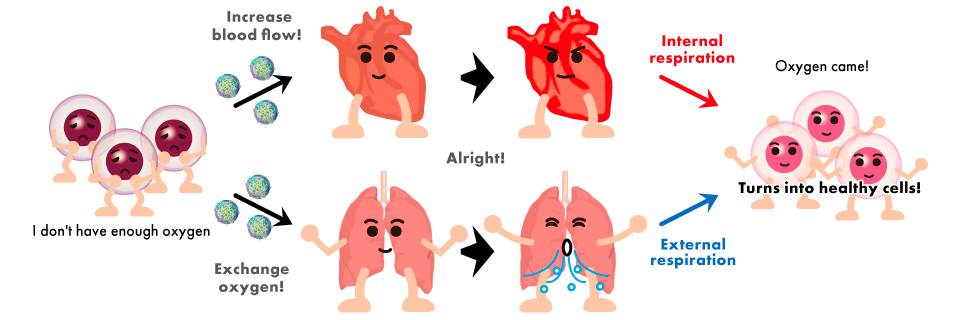
It has been shown that cells communicate directly with each other via exosomes (good exosomes) and move each organ properly in order for the body to function normally and maintain a healthy state.
On the other hand, it has been found that exosomes are also abused (bad exosomes) for cancer cell metastasis.
Mechanisms of Cancer Metastasis
In cancer cell metastasis, there has been a phenomenon that has been said to be the “biggest mystery of cancer metastasis” for many years.
This is a phenomenon in which fibroblasts, blood vessels, lymph vessels change in the metastasized tissue before the cancer cells metastasize, and are set up to accept the cancer cells. In fact, it turned out that exosomes are involved in this phenomenon.
Good Exosomes and Bad Exosomes
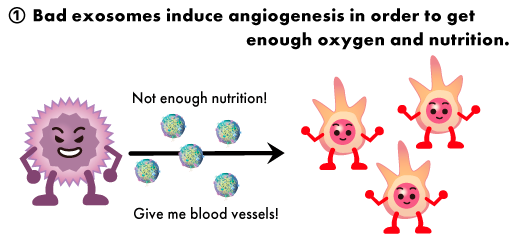
①Cancer cells use exosomes (bad exosomes) to pull blood vessels out of the surrounding area because blood vessels are hard to reach the center when the tissue increases in size.
This angiogenesis is one of the behaviors that cancer tissues always show.

②After angiogenesis, cancer cells detached from the primary lesion enter large
blood vessels through the drawn capillaries and move to other organs.
At this time, cancer cells use exosomes to evade immune function by sending a message to immune
cells saying that they are not enemies.
In other words, cancer cells first released exosomes into the tissues they
metastasized to create an environment in which cancer cells could easily settle in advance, and
then guide cancer cells that come later to obtain a new activity base.
The discovery of the mechanisms of cancer cell metastasis using this exosome is expected to be a
tremendous breakthrough in future cancer research.
Professor Ochiya's Research Project

Currently, Professor Ochiya is at the forefront of exosome research and leads the world. He is a project leader at the Division of Molecular and Cellular Medicine, National Cancer Center Research Institute and is working on novel diagnostic and therapeutic methods for various diseases including cancer.
By constantly challenging the development of new fields based on experiences accumulated in areas such as nucleic acid pharmaceuticals, bioimaging, stem cells, regenerative medicine, cell engineering, and molecular oncology, we have advanced nucleic acid pharmaceuticals to physician-initiated clinical trials and developed the practical development of microRNA preclinical studies and body fluid diagnostics so far.
In fact, the elucidation of the mechanisms of cancer metastasis by microRNAs encapsulated in exosomes secreted by cancer cells has produced a "cancer diagnosis" that has a high level of sensitivity and specificity in a different dimension from conventional "cancer diagnosis" and allows ultra-early detection.
Furthermore, since the role of exosomes has been elucidated in various diseases other than cancer, the development of new therapeutic methods targeting exosomes is drawing attention from all over the world as the latest research area.
.jpg)
.png)